COMPARATIVE PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION - DEFINITION:
Comparative public administration is defined as
the study of administrative systems in a comparative fashion or the study of
public administration in other countries.
Another definition for
"comparative public administration" is the "quest for patterns
and regularities in administrative action and behavior".
It looks to test
the effectiveness of the Classical Theorists' (Fayol,Taylor,Urwick,etc)
Principles of Administration effectiveness on a universal level(different
political and administrative setups in developing and developed countries and
their ecology) as well as develop a comparative theory of Public
Administration.
It is a very significant area of study in Public
Administration as it helps in understanding Administrative setups and their
functioning in various settings and societies/countries and what works and
why it works. Also,it helps improvise administrative systems making them more
efficient together with helping in adding and improvising the
already existing literature/theories of Public Administration thus leading to a
strong and practical theory of the subject with the help of practical
experiments and analysis.
COMPARATIVE PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION EVOLUTION -
A BACKDROP:
Even though comparative studies in
administration date back to Aristotlian times where he sent scholars to
different parts of world to study their political systems,Comparative Public
Administration started off as a topic of interest post the Wilson(called the
1st comparativist) essay in 1884 where he very rightly stated that in
order to know our own country's administrative weaknesses and virtues we need
to compare with others. And,he stated that administration is the best and most
safe prospect of comparative studies as administrative techniques and
procedures are similar almost everywhere and in fact we can learn a
lot by comparing.
However,it was not taken so seriously due to the
the emphasis on conceptualising and structuring as well as defining Public
Administration at that time was the top priority.
- The theorists and administrators
as well as governments were busy understanding their own administrative setup
before they could set off on a comparison with others.
- So, while this was being
contemplated the First World War erupted and with its end and the establishment
of the League Of Nations there came about a lot of questions regarding the
need to understand the needs of the countries who were not so developed because
many of them came under the British colonialism as well as other imperialist
countries in order to control these and draw maximum benefit.
Philosophical turn to CPA !!!
This comparative study took a philosophical turn
during the course of the second world war and its aftermath when
there came the end of imperialism and colonialism and emergence of
many independent states, a joint initiative by the developed countries
under the United Nations(formerly called 'The League Of Nations') aegis to
refurbish the developing an third world countries as well as to develop their
own war damaged national economies. And lets not forget the beginning of Cold
War between the two superpowers USA and Soviet Union which played a big part in
this movement where both looked to hegemonise the world politics and economy.
- USA took the lead here in administrative
studies and also in providing financial as well as technical help to the
developing nations in order to increase their market share and also to
curb communism that was a product of the Soviet Union.
The USA was the hub of these studies since the
Western countries lacked the institutional and administrative capacities to
implement their development plans post world war 2.
- The government,United
Nations and various private institutions as well as corporates sponsored varied
technical assistance programmes that enabled the public
administrators,lecturers of public administration and professionals to study
the same in depth as well as travel abroad and gather hands on experience and
build a universal comparative theory of Public Administration. Notable in
these efforts were that of the American Society For Public Administration(ASPA)
& American Political Science Association( APSA).
The first organisation formally formed to
formulate a universal comparative theory of public administration was the
Comparative Administration Group(CAG) in 1960 that was a division of the ASPA ,
funded by the Ford foundation to study methods for improving public
administration in developing countries under the chairmanship of Fred W. Riggs.
- More than providing administrative techniques this group became a forum for
intellectuals to understand why the developing countries differ so much in
practise of administration and are not able to sustain the classical theory
principles of administration in their systems even though Classical theorists
of administration like Fayol & Weber , etc preached that their principles
and models of administration were universal in their element and can be applied
anywhere with greatest success.
CAG gave the idea of scientific studies and
emphasised on empirical and ecological(social,cultural and historical
factors) study of various administrative systems.
Even though the CAG had
to shut shop in the early 70's since various administrators and
academicians realised that due to the highly complex setting which the group
had provided for comparative Public Administration studies was resulting in
failures in providing really empirical assessment of administration factors in
a society.
They stated that it provided a very good direction but the
techniques were not being specified to execute the idea. And so the studies was
transferred back to the Department of Comparative Studies.
Also in 1968, the first Minnowbrook Conference
was held under the chairmanship of Dwight Waldo that also talked about the
need for Comparative Public Administration study and analysis.
Now we will discuss in detail.
APPROACHES TO THE STUDY OF COMPARATIVE PUBLIC
ADMINISTRATION:
1) Ideal or
Bureaucratic Approach:
- Bureaucratic
specifications are studied for reaching conclusions and developing
understanding.
- Under this approach structures of organisations are analysed in
terms of their horizontal differentiation,vertical differentiation,span of
control,etc.
- Procedures and rules are analysed and the framework of functioning
is determined.
- Job specifications and descriptions at various nodes are
analysed and some understanding is reached on the basis of elaborateness and
degree of specialisation compared in regards to different administrative
systems.
The limitations of this approach is that though
it has been considered simple but it does not explain the structures and their
functions in society and gives a very general observation.
2) Structural - Functional Approach :
It is a very significant area of study in Public Administration as it helps in understanding Administrative setups and their functioning in various settings and societies/countries and what works and why it works. Also,it helps improvise administrative systems making them more efficient together with helping in adding and improvising the already existing literature/theories of Public Administration thus leading to a strong and practical theory of the subject with the help of practical experiments and analysis.
COMPARATIVE PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION EVOLUTION - A BACKDROP:
However,it was not taken so seriously due to the the emphasis on conceptualising and structuring as well as defining Public Administration at that time was the top priority.
This comparative study took a philosophical turn during the course of the second world war and its aftermath when there came the end of imperialism and colonialism and emergence of many independent states, a joint initiative by the developed countries under the United Nations(formerly called 'The League Of Nations') aegis to refurbish the developing an third world countries as well as to develop their own war damaged national economies. And lets not forget the beginning of Cold War between the two superpowers USA and Soviet Union which played a big part in this movement where both looked to hegemonise the world politics and economy.
Also in 1968, the first Minnowbrook Conference was held under the chairmanship of Dwight Waldo that also talked about the need for Comparative Public Administration study and analysis.
APPROACHES TO THE STUDY OF COMPARATIVE PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION:
 |
It is considered as a very popular approach for comparing various
administrative systems and was implemented by Fred W. Riggs in his study for
developing his Models of society/environment/ecology which will be discussed
later in this article.
This approach analyses society in terms of its various
structures and their functions for reaching an understanding regarding their positioning
and functioning.
- Structures here can refer to govt.(political arrangement) and
abstract like values systems in society.
- Function is seen as the discharge of
duties by these structures in the society.
The limitation of this approach is that there
has to be a correct identification of the structures before proceeding to
analyse them especially in agraria-transitia and fused-prismatic societies.
3) Ecological Approach:
- Devised by Riggs this approach states that structures and their
functions exist in an inter dependant manner.
- So if a study is to be undertaken
of a particular structure and its function then its effects on other systems
and their functions of society are also to be analysed.
- Limitations is that
this approach is highly complex and difficult to apply.
HISTORICAL AND SOCIOLOGICAL FACTORS AFFECTING
ADMINISTRATIVE SYSTEMS:
If one notices carefully then it is clearly
evident that historical events have led to the invention of many administrative
practises. Though there are aplenty,however,some examples are cited below.
1) English Administrative system:
- England does not possess a written constitution mainly because it was a
monarchy prevailing there and the people lived there through conventions
and traditions going on from time immemorial.
2) Indian Administrative system:
- Reservations are made as Indian society is very diverse in matters of
social as well as economic status,etc after a lot of historical events like B.R Ambedkar and his policies as well as the British division of Hindu and
Muslims and other minorities in separate electorate system,etc.
- There are
various social laws in India that are made from society like Panchayats,etc.
- Tribal welfare is given special attention in India due to existence of tribals
in the society.
- Many offices(bureaucratic,political,economical,etc) are
remnants of British legacy like the office of the collector,police dept,civil
services,etc.
- Revenue administration here is a modern version inspired by
historic Mughal ones.
3) USA Administrative system:
- Many historical and sociological factors have also shaped the American
system.
- A few of them cited are the Civil war that lead to providing African
American slaves were given the title of citizens and right to vote.
- Also the
second civil rights movement that occurred under the aegis of Martin Luther
King Jr. leading to elimination of segregation and racial discrimination
between black and white Americans.
4) France Administrative system:
- Arrangement of Droit Administration could be seen associated with the
approach and functioning of Napoleon Bonaparte who set the table for a
centralised administration as an efficient administration.
- The storming of
Bastille incident which was fuelled by economic crisis lead to the overthrow of
monarchy there to republican system and led to the establishment of Declaration
of the Rights of Man and the Citizen that lead to the first step of France's
constitution framing.
ADMINISTRATION AND POLITICS IN DIFFERENT COUNTRIES:
1) USA:
- The USA have a federal republican form of government where President is
the national as well as executive head. There is a separate constitution(which
bears allegiance to the federal constitution of 1787) as well as
citizenship for every state and they are all bound together in a federation,thus
all working as a whole with their autonomy intact.
- The Constitution of US
specifies the subjects listed for the national/federal and the ones reserved
for the States and also the residuary powers lie with the states only.
- There are
three level of governments - national or federal,state and
local(counties,townships,cities,etc).
- Separation of powers between the
legislature,executive and judiciary is an important aspect.
- The Senate (Upper
House) and House of Representatives(Lower house) comprise the congress/legislature
of the country.
- There is no specificity in the constitution regarding the
administrative system but it does state that the President can from time to
time as and when necessary get advise from the principal officers of the
various departments regarding his duty as the chief executive of those
departments.
- There are thirteen departments in the administration that come
under the direct control of the President.
- The President however does not
possess the authority to change/reorder his cabinet as that power lies with the
Congress.
Civil services in USA are also done on merit
through competitive exams and also at times there are some political appointees
too who are chosen by the president for their extraordinary achievement in a
particular field suitable to the job. Some departments are headed by
individuals whereas some are headed by Boards and Commissions.
2) UK:
If one notices carefully then it is clearly evident that historical events have led to the invention of many administrative practises. Though there are aplenty,however,some examples are cited below.
It is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy. In practise it is a Parliamentary democracy. The Monarch is the head and performs functions akin to the President of India.
Legislature is supreme and is bicameral viz. House of
Lords(upper house) and House of Commons(lower house). Executive is headed by
the political executive that is the Prime Minister and his cabinet that consist
of ministries staffed by civil servants under ministers. Boards and commissions
are formed to operate and regulate various industries and
services. Judiciary is independent.The House of Lords is the highest court
of appeal for civil cases and some criminal cases.
The Senior Courts of England and Wales were
originally created by the Judicature Acts as the "Supreme Court of
Judicature". It was renamed the "Supreme Court of England and
Wales" in 1981, and again to the "Senior Courts of England and
Wales" by the Constitutional Reform Act 2005. It consists of the following
courts:
·
Court of Appeal- Deals only
with appeals from other courts or tribunals. The Court of Appeal consists of
two divisions: the Civil Division hears appeals from the High Court and County
Court and certain superior tribunals, while the Criminal Division may only hear
appeals from the Crown Court connected with a trial on indictment (i.e., for a
serious offence). Its decisions are binding on all courts, including itself,
apart from the Supreme Court.
·
High Court of Justice - The High
Court of Justice functions, both as a civil court of first instance and a
criminal and civil appellate court for cases from the subordinate courts. It
consists of three divisions: the Queen's Bench, the Chancery and the Family
divisions. The divisions of the High Court are not separate courts, but have
somewhat separate procedures and practises adapted to their purposes. Although
particular kinds of cases will be assigned to each division depending on their
subject matter, each division may exercise the jurisdiction of the High Court.
However, beginning proceedings in the wrong division may result in a costs
penalty.
·
Crown Court- is a
criminal court of both original and appellate jurisdiction which in addition
handles a limited amount of civil business both at first instance and on
appeal.The Crown Court is the only court in England and Wales that has the
jurisdiction to try cases on indictment and when exercising such a role it is a
superior court in that its judgements cannot be reviewed by the Administrative
Court of the Queen’s Bench Division of the High Court.
The Crown Court is an inferior court in respect of the other work it
undertakes, viz. inter alia, appeals from the Magistrates’ courts and other
tribunals.
Civil servants are recruited through merit via open
competitive exams.
3) FRANCE:
- It is a mixture of Republican as well as Parliamentary form of govt.
- President is the Chief executive and enjoys tremendous powers in the legislature
as well as Parliament.
- Here the President is directly elected by the people.
- The
Prime Minister is then chosen and appointed as per the President's wish from
the Parliament.
- The Prime Minister has to enjoy the confidence of both the
President and the Parliament in order to sustain his position.
- Executive is
separated from legislature and thus the President is not able to influence the
executive much but still indirectly the PM has to go by him to enjoy his
confidence because most of the times,the parliament and the president are from
the same party.
Civil services are of two types External recruitment and
internal recruitment where external recruitment is done through open
competitive exams for graduates under 27 years of age and the internal recruitment
is for people from the lower echelons of service having at least five years of
service and not more than 36 years old.
- They are then chosen and trained at the
Ecole Nationale Administration for two years.
4) JAPAN:
The Constitution of Japan rests on three principles -
a) sovereignty of people ,
b) guarantee of Fundamental Rights,
c)
renunciation of war.
The Emperor performs the role akin
to Indian president. The Japanese people elect their representatives to the
Japanese Parliament called Diet which is bicameral that is, House of
Councillors and the House Of Representatives.
Both Houses share equal powers
but the house of representatives has superiority in matters of finance. The
prime minister is appointed by the prime minister from the Diet who heads the
executive and also the Emperor appoints the chief judge of the supreme
court. Grants are to be passed by the Diet and then only it is given to the
executive. Local govt possess autonomy in its matters. People posses the right
to choose their public officials as well as remove them.
Civil services are of
two types here -
a) Special govt service - includes members of cabinet approved
by the Diet like positions of high officials in Imperial
Court,Judges,Ambassadors and Ministers,Diet employees,common labourers and
employees of state corporations.
b) Includes personnel of National
govt.,administrative as well as clerical except the Special govt. services
ones.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEMOCRACY AND REPUBLIC:
Democracy and Republic are two forms of
government which are distinguished by their treatment of the Minority, and the
Individual, by the Majority.
- In a Democracy, the Majority has unlimited power
over the Minority. This system of government does not provide a legal safeguard
of the rights of the Individual and the Minority. It has been referred to as
"Majority over Man".
- In a Republic, the Majority is Limited and
constrained by a written Constitution which protects the rights of the
Individual and the Minority. The purpose of a Republic form of government is to
control the Majority and to protect the God-given, inalienable rights and
liberty of the Individual.
The United States of America is founded as
a Republic under the Constitution. The Ministers head Ministries with directors
under them to carry out execution and also to advise the Minister.
******CURRENT STATUS OF COMPARATIVE PUBLIC
ADMINISTRATION:
After the decline of the comparative
administration group (CAG) in the early 1970's,there was a lull in this field
due to many factors like theoretical and fact based study was only done and so
there was problem in the applicability of those models and USA was going
through a bad phase in the Vietnamese war and so funds had to be diverted,etc.
- However, it got a boost once again when scholars
like Robert Dahl,James Cloeman,Rapheli,Dwight Waldo etc propagated it and
stated that without comparison there can never be a science of administration.
- Also the behavioural school of thought was bringing in a lot of attention to
the fact and value theories of administrative man and so comparative public
administration saw a resurgence.
- In the 80's and 90's studies in CPA resurfaced
but with a new objective,philosophy and orientation than its previous
predecessors and counterparts. It started to study various arrangements like
RTI,Rule of Law,good governance,etc in different countries. It has recently
started focusing itself on the analysis of such operations of administrative
systems which affect functioning of various societies.
The following could be seen as the recent trends
in the studies of Comparative Public Administration:
1) Studying the status of human rights in the
nations of the problems associated with human rights.
2) Studying the status of Rule of Law and
analysing the barriers if any.
3) Studying the presence of Civil Society
Institutions and their role and contribution in the administrative arrangements
of societies.
4) Studying the level of participation and
involvement in the implementation of schemes related to welfare of people.
5) Studying the presence of arrangements
through which accountability of politicians and administrators could be ensured
towards the public through the mechanisms prescribed and available like
RTI,Citizens charters,Ombudsman,Social Audit,etc.
ECOLOGY AND ADMINISTRATION:
The Crown Court is an inferior court in respect of the other work it undertakes, viz. inter alia, appeals from the Magistrates’ courts and other tribunals.
3) FRANCE:
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEMOCRACY AND REPUBLIC:
- Ecology in simple words relates to
'Environment'. And this environment includes physical,social and cultural
aspects. So, basically we are going to talk about the relationship between
administration and the environment it is set in(internal as well as
external) and how the affect each other.
- Environment is the largest system,the rest and
others like political systems,administrative systems,etc are all sub systems
who work under it. It influences its sub systems and vice versa. They both have
to adjust to each other and also reform and change each other from time to time
to stay up to date where the people's wishes drive the policies and the
policies bring in development that uplifts the socio-economic status and level
of the environment for progress. So they are interdependent and not mutually
exclusive of each other.
Administration is seen as one of the most
significant aspect of any societal arrangement as it makes possible the
achievement of governmental function fulfilment. It has been observed that
administration of any state happens to be an expression of various unique
factors existing in society and is inter dependant over other arrangements in
the society that provides the stability of all structure in a society.
Various scholars like George Orwell in their writings like 'Shooting an Elephant' books have given case studies of how they have seen practically that the administrative systems in different parts of the world perform differently in order to suit the environment or ecology they are set in.
The ecological approach to Public Administration
was first propagated popularly by Fred W. Riggs who studied administrative
systems in different countries( emphasis on developing countries) and why there
was a vast amount of disconnect among them while applying the Americanised
theories of Public Administration and how they coped up. He found that the main
reason for this uniqueness of administrative systems in the world is the
environment that they are set in. Each country had a different environment
setting and that played a major role in the shaping of the administrative
system because without the help and approval of its people an administrative
system cannot survive and thus it acts according to its environment and in turn
it also influences the society with its work and procedures.
Max Weber
- projected an ideal system of
bureaucracy where bureaucracy was shown as a closed system unaffected by the
environment.
- A system which Weber assumed would be applicable and successful in
all countries irrespective of its socio economic status and that's where he
went wrong because we can very well see that the systems in USA and UK etc
cannot be applied in an environment of India or any other developing countries.
- Weber did provide a very good structure for the organisation of bureaucracy but
the part which he missed as cited above was the starting ground for Riggs when
he began his research on the relationship between ecology and administration.
Ecology/Environment affects the administrative
system both internally as well as externally.
Internally, it affects when we take note that in actuality the administrator is a man of society and thus when he is taking an administrative decision,he will definitely be influenced by his values,societal and cultural attitude,etc to quite an extent and that needs to be taken into account.
Externally, also the ecology/environment affects
the administrative organisation by
- means of social values and rules,
- culture
of the society,
- dependence on other important subsystems prevalent in the
society,etc
where the administration and politics have to be in context of the
people's wishes and demands and if they go against it will face a possibility
of overthrow and revolt anytime.
Therefore,one can very conveniently understand
from the above mentioned,the delicate and crucial relationship between Ecology
and Administration.
RIGGSIAN MODELS AND THEIR CRITIQUE:
Riggs is considered the pioneer in the field of
Ecological Approach to Public Administration. He stated that if studies of
Public Administration had to become really comparative then it has to shift
from being Normative(Establishing, relating to, or deriving from a standard or
norm, esp. of behavior) to empirical (Based on, concerned with, or
verifiable by observation or experience rather than theory or pure logic), from
Ideographic(case by case study and not related to one another) to
nomothetic(relating to the study or discovery of general scientific laws) and
from non ecological(closed and confined to one area) to ecological(open and
cross cultural).
- He blamed the import of developed countries'
administrative practices as it is by the developing countries for their
progress without any study as the reason for its failure and the reason for
developing countries still lagging behind.
- In his ecological studies he gave the concept of
structural functional approach as a means to study the environment and
administration relation. According to this approach every society has various
structures that perform specific functions like
political,economic,social,symbolic and communicational functions in the
society.
On the basis of this approach he proceeded to
study and listed two theoretical models to explain the administrative systems
in the comparative context. Those models are:
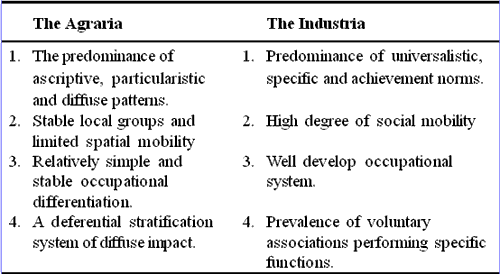
a) AGRARIA MODEL:
- It is the Agricultural society and the characteristics are functional
diffusion,particularistic norms,self sufficiency,ascriptive.
- The attribution of
something to a cause) values,stable local groups and limited or no
mobility,differentiated stratification.
- Agraria is agriculture dominated
society and Riggs takes China at the time for instance Imperial China.
- In
Agrarian primordial preferences like caste and given priority.
- Occupational
pattern is fixed that is Agriculture and carries on for many generations.
- Very
few administrative structures and their functions/duties were not at all specified.
b) TRANSITIA MODEL :
- It is the in between society. It is in between or lets use the term in
transition between the Agraria and Industria society and bears features
resembling to both.
- It is on the path to become a developed society from an
agricultural society. Examples are India,Thailand,etc.
c) INDUSTRIA MODEL:
- It refers to a developed or Industry dominated society.
- Its
characteristics are Universalistic norms,Achievement values,specific
patterns,high degree of social and spatial mobility,well-developed occupational
system,egalitarian class system,prevalence of associations which are
functionally specific and non ascriptive.
- USA is an example of this society.
 |
LIMITATIONS AND CRITIQUE OF RIGGS' AGRARIA-TRANSITIA-INDUSTRIA MODEL:
1) It does not help in examining the
transitional societies and is too rigid focusing only on the underdeveloped and
developed countries.
2) It does not provide sufficient mechanism to
study mixed-type societies. Critics argue that the industrial societies will
always retain or have some agrarian features.
3) It assumes a unidirectional movement from an
agraria stage to an industria stage.
4) Its major stress is on the environment of the
administrative system but not on the administrative system per se.
5) It is too general and abstract with little
resemblance to concrete reality.
Consequently Riggs abandoned this typology and
proceeded to better it and that resulted in a new typology/model he designed
which was the Fused-Prismatic-Diffracted Model.
RIGGS IMPROVISED TYPOLOGY :
FUSED-PRISMATIC-DIFFRACTED MODEL:
It is the more improvised and
specified version of his previous typology where the Fused society can be
compared to the agrarian model,the prismatic society can be compared to the
Transitia model and the Diffracted society can be compared to the Industria model.
This Model was designed to silence those critics
who stated that Riggs had not effectively and in detail specified the
'Transitia' society which was very important as most of the world in in that
phase.
This model effectively detailed all of the typologies.The
new model is based on the principle of a prism and how it diffracts fused
colours of white light back into the seven colours of the spectrum when
passed through it. White light represents a society with very less degree of
specialisation and development and the diffracted spectrum reflects the highly
specialised and developed society. The in between prismatic society is the
transition society.
He stated that neither of the extreme sides
exist in totality or as it is but yes,it is certain that they do but in varying
degrees as suitable to the environment/ecology.
First we will discuss the Fused and Diffracted
model and then proceed to explain the Prismatic model. A good understanding of
the Fused and Diffracted Model will only be the tool to understand the
Prismatic Model features.
FUSED MODEL(Ex- Imperial China and
Thailand):
1) Heavily dependent on agriculture.
2) Economic system based on barter system.
3) King and officials nominated by the king
carry out all administrative,economic and other activities.
4) Royal family and special sects dominate.
5) Ascriptive values dominate.
6) Having many administrative structures that
are part diffracted(perform special functions they are given charge of) and
part fused ( many structures performing many functions which are not prescribed
to them thus overlapping with the diffracted ones and confusing the system).
DIFFRACTED MODEL:
1) It is the polar opposite of the fused
society. Each structure carries out its own functions.
2) Attainment value in society.
3) Economic system based on market
mechanism(demand and supply)
4) Responsive government
5) General consensus among all the people on all
basic aspects of social life.
PRISMATIC MODEL(Example
India,Thailand,etc):
1) In real no society is completely fused or
completely diffracted. A prismatic society has achieved a certain degree of
differentiation or specialisation.
2) Heterogeneity - Simultaneous existence of
different kinds of system and viewpoints. Example - rural-urban,Indian gurukuls
- western education,homoeopathic-allopathic. Various factors pulling the
system apart. Political and administrative officers enjoy enormous influence.
Privileges for select groups which may be communal thus creating problem in
administration.
3) Formalism(Excessive adherence to prescribed
forms) - Discrepancy between formally prescribed and effectively practiced
norms. Rules and regulations are prescribed but wide deviations are observed.
Lack of pressure on govt. for programme objectives. Weakness of social powers
to influence bureaucratic performance. Hypocrisy in social life. Constitution
formalism which means that there is a gap between stated principles and actual
implementation.
4) Overlapping - Differentiated structures
coexist with undifferentiated structures of Fused type. New or modern social
structures are created,but traditional social structures continue to dominate.
Example - Parliament,Govt,Offices exist but behaviour is still largely governed
by family,religion,caste,etc.
SUB-SYSTEMS OF THE PRISMATIC MODEL:
1) Administrative
subsystem which is called the SALA MODEL (The Spanish word, 'Sala',
has a variety of meanings like a government office, religious conference, a room, a pavilion, etc.
The word, 'Sala', is also generally used in East Asian countries more or less with the same
meaning.): -
a) Certain features of bureau ( diffracted
) coexists with certain features of chambers ( fused ).
Formalism exists:
1.a. Universalizaiton of
law is there but is not followed.
1.b. Objective is social welfare but priority is
personal aggrandizement.
b) Overlapping exists:Highly concentrated
authority structure overlaps with localized and dispersed control system.
c) Non cooperation among rival communities also
reflects in administration. So favouritism and nepotism is widespread
d) Existence of clects – The dominant group who
use modern methods of organization but retains diffuse and particularistic goal
of traditional type.
e) For promotion officers depend on ascriptive
ties . Officers unresponsive to people . Unbalanced polity in which bureaucracy
dominates exists.
f) Nepotism, corruption and inefficiency.
2) Economic subsystem which is also
called the BAZAAR - CANTEEN MODEL:
a) Market factors ( demand and supply ) as well
as area factors ( religious, social, family) dominates the economy.
b) This leads to price indeterminacy further
deteriorating economic conditions encouraging black marketing,
hoarding,adulteration etc.
c) Foreign domination and a small section of
people dominate economic institution.
d) Price of services vary from place to place,
time to time and person to person.
e) Economic subsystem acts like subsidized
canteen to privileged & tributary canteen to members of less priviledged,
politically non influential or members of outside group.
f) Wage relation: Wide gap exists for same work.
Persons with less wage may feel motivated to earn more by illegitimate means.
DEVELOPMENT MODEL:
- Rising level of diffraction represents
development.
- Higher the level of differentiation ( various structures for
various functions ) and integration (coexistence of these structures ),higher
the development.
If differentiation is high but no sufficient
integrative mechanism , it leads to confusion and chaos.
Differentiation depends upon technological
factors.Integration depends upon:
1.a. Penetration – receptivity of law and govt.
willingness and ability.
1.b. Participation - willingness of people to
participate.
CRITICISM OF RIGGS'
FUSED-PRISMATIC-DIFFRACTED MODEL:
1) Usage of scientific words does not make
administration science.
2) It has highly technical description.
3) Prismatic and sala models are equilibrium
models and does not lead to social change.
4) Lack of measurement of level of diffraction
in prismatic or diffracted society.
5) Diffracted society is also not desirable
because it is static and in equilibrium.
6) Difficult to identify the level of
differentiation and integration for development.
7) Lack of international perspective.
8)Wrong analytical tool.
9) Fails to explain the role of administration
in society.
10) Overlapping is not specific phenomena of
prismatic society but exists in diffracted society also.
11) Prismatic model has a negative character.
Irrespective of the criticism Riggs attracted
there is no denying that he set the table and standards for Comparative Public
Administration and got to the root of the failure of Americanised and Europised
Public Administration practices failing in developing countries, through
his important paradigm called ''The Ecological approach to Public
Administration'',and also suggested the issues that plague the developing
countries and how to rectify them.
It is the more improvised and specified version of his previous typology where the Fused society can be compared to the agrarian model,the prismatic society can be compared to the Transitia model and the Diffracted society can be compared to the Industria model.
This Model was designed to silence those critics who stated that Riggs had not effectively and in detail specified the 'Transitia' society which was very important as most of the world in in that phase.
This model effectively detailed all of the typologies.The new model is based on the principle of a prism and how it diffracts fused colours of white light back into the seven colours of the spectrum when passed through it. White light represents a society with very less degree of specialisation and development and the diffracted spectrum reflects the highly specialised and developed society. The in between prismatic society is the transition society.
He stated that neither of the extreme sides exist in totality or as it is but yes,it is certain that they do but in varying degrees as suitable to the environment/ecology.
First we will discuss the Fused and Diffracted model and then proceed to explain the Prismatic model. A good understanding of the Fused and Diffracted Model will only be the tool to understand the Prismatic Model features.
FUSED MODEL(Ex- Imperial China and Thailand):
1) Heavily dependent on agriculture.
2) Economic system based on barter system.
3) King and officials nominated by the king carry out all administrative,economic and other activities.
4) Royal family and special sects dominate.
5) Ascriptive values dominate.
6) Having many administrative structures that are part diffracted(perform special functions they are given charge of) and part fused ( many structures performing many functions which are not prescribed to them thus overlapping with the diffracted ones and confusing the system).
DIFFRACTED MODEL:
1) It is the polar opposite of the fused society. Each structure carries out its own functions.
2) Attainment value in society.
3) Economic system based on market mechanism(demand and supply)
4) Responsive government
5) General consensus among all the people on all basic aspects of social life.
PRISMATIC MODEL(Example India,Thailand,etc):
1) In real no society is completely fused or completely diffracted. A prismatic society has achieved a certain degree of differentiation or specialisation.
2) Heterogeneity - Simultaneous existence of different kinds of system and viewpoints. Example - rural-urban,Indian gurukuls - western education,homoeopathic-allopathic. Various factors pulling the system apart. Political and administrative officers enjoy enormous influence. Privileges for select groups which may be communal thus creating problem in administration.
3) Formalism(Excessive adherence to prescribed forms) - Discrepancy between formally prescribed and effectively practiced norms. Rules and regulations are prescribed but wide deviations are observed. Lack of pressure on govt. for programme objectives. Weakness of social powers to influence bureaucratic performance. Hypocrisy in social life. Constitution formalism which means that there is a gap between stated principles and actual implementation.
4) Overlapping - Differentiated structures coexist with undifferentiated structures of Fused type. New or modern social structures are created,but traditional social structures continue to dominate. Example - Parliament,Govt,Offices exist but behaviour is still largely governed by family,religion,caste,etc.
SUB-SYSTEMS OF THE PRISMATIC MODEL:
1) Administrative subsystem which is called the SALA MODEL (The Spanish word, 'Sala', has a variety of meanings like a government office, religious conference, a room, a pavilion, etc. The word, 'Sala', is also generally used in East Asian countries more or less with the same meaning.): -
a) Certain features of bureau ( diffracted ) coexists with certain features of chambers ( fused ).
Formalism exists:
1.a. Universalizaiton of law is there but is not followed.
1.b. Objective is social welfare but priority is personal aggrandizement.
b) Overlapping exists:Highly concentrated authority structure overlaps with localized and dispersed control system.
c) Non cooperation among rival communities also reflects in administration. So favouritism and nepotism is widespread
d) Existence of clects – The dominant group who use modern methods of organization but retains diffuse and particularistic goal of traditional type.
e) For promotion officers depend on ascriptive ties . Officers unresponsive to people . Unbalanced polity in which bureaucracy dominates exists.
f) Nepotism, corruption and inefficiency.
2) Economic subsystem which is also called the BAZAAR - CANTEEN MODEL:
a) Market factors ( demand and supply ) as well as area factors ( religious, social, family) dominates the economy.
b) This leads to price indeterminacy further deteriorating economic conditions encouraging black marketing, hoarding,adulteration etc.
c) Foreign domination and a small section of people dominate economic institution.
d) Price of services vary from place to place, time to time and person to person.
e) Economic subsystem acts like subsidized canteen to privileged & tributary canteen to members of less priviledged, politically non influential or members of outside group.
f) Wage relation: Wide gap exists for same work. Persons with less wage may feel motivated to earn more by illegitimate means.
DEVELOPMENT MODEL:
- Rising level of diffraction represents development.
- Higher the level of differentiation ( various structures for various functions ) and integration (coexistence of these structures ),higher the development.
If differentiation is high but no sufficient integrative mechanism , it leads to confusion and chaos.
Differentiation depends upon technological factors.Integration depends upon:
1.a. Penetration – receptivity of law and govt. willingness and ability.
1.b. Participation - willingness of people to participate.
CRITICISM OF RIGGS' FUSED-PRISMATIC-DIFFRACTED MODEL:
1) Usage of scientific words does not make administration science.
2) It has highly technical description.
3) Prismatic and sala models are equilibrium models and does not lead to social change.
4) Lack of measurement of level of diffraction in prismatic or diffracted society.
5) Diffracted society is also not desirable because it is static and in equilibrium.
6) Difficult to identify the level of differentiation and integration for development.
7) Lack of international perspective.
8)Wrong analytical tool.
9) Fails to explain the role of administration in society.
10) Overlapping is not specific phenomena of prismatic society but exists in diffracted society also.
11) Prismatic model has a negative character.
Irrespective of the criticism Riggs attracted there is no denying that he set the table and standards for Comparative Public Administration and got to the root of the failure of Americanised and Europised Public Administration practices failing in developing countries, through his important paradigm called ''The Ecological approach to Public Administration'',and also suggested the issues that plague the developing countries and how to rectify them.
