Define the term 'disaster' and describe its classification.
Disaster is a sudden, calamitous event bringing great damage, loss, and destruction and devastation to life and property. The damage caused by disasters is immeasurable and varies with the geographical location, climate and the type of the earth surface/degree of vulnerability. This influences the mental, socio-economic, political and cultural state of the affected area. Generally, disaster has the following effects in the concerned areas.
1. It completely disrupts the normal day to day life
2. It negatively influences the emergency systems
3. Normal needs and processes like food, shelter, health, etc. are affected and deteriorate depending on the intensity and severity of the disaster.
TYPES OF DISASTER
Generally, disasters are of two types – Natural and Manmade. Based on the devastation, these are further classified into major/minor natural disaster and major/minor manmade disasters. Some of the disasters are listed below,
| Major natural disasters:
· Flood
· Cyclone
· Drought
· Earthquake
|
Minor natural disasters:
· Cold wave
· Thunderstorms
· Heat waves
· Mud slides
· Storm
|
Major manmade disaster:
| Minor manmade disaster:
· Road / train accidents, riots
· Food poisoning
· Industrial disaster/ crisis
· Environmental pollution
|
What is Disaster Management Cycle ?

- How would you define vulnerability?

- Vulnerability
is the characteristics and circumstances of a community, system or asset
that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard.
- There
are many aspects of vulnerability, arising from various physical, social,
economic, and environmental factors.
- Examples
may include poor design and construction of buildings, inadequate
protection of assets, lack of public information and awareness, limited
official recognition of risks and preparedness measures, and disregard for
wise environmental management.
- Vulnerability
varies significantly within a community and over time.
- This
definition identifies vulnerability as a characteristic of the element of
interest (community, system or asset) which is independent of its
exposure.
- However,
in common use the word is often used more broadly to include the element's
exposure.
What is Total Disaster Risk Management Approach?- Total Disaster risk management approach is to understand
the disaster and areas prone to it and prevent loss to human and
property.
- Although a few countries have adopted risk management
concepts and principles in disaster management, most countries, especially
developing countries, remain unfamiliar with this approach.
- The prevailing practices, particularly in Asia, are more
inclined towards managing response to disasters (which requires
preparedness) than towards managing risks and the underlying conditions
that lead to disasters (which requires, among others, risk assessment,
vulnerability reduction, and capacity enhancement).
- However, the terms “risk” and “total” have become
management. science jargons whose application to disaster management
should be examined and explained well in order for them to be effectively
communicated to policy- makers &d the general public.
- In this regard, the concept of “risk”, which in
science connotes probability, needs to be understood adequately (and not
to be confused with hazard). Also, the concept of “total”, which has been
widely used in the context of total quality management, needs to be
developed as it relates to disaster risk management.
- Since these have become the 1ingo”l of industrial, business
and management professionals, the development and promotion of the total
disaster risk management approach could enable professionals previously
less concerned to have meaningful involvement in disaster management.
**********************************************************************************************************************************What are the major features of Emergency Operations Centre It has been observed that at the time of a calamity/disaster, communication services are the first to go out of order. It has therefore been decided to put in place multi-mode and multi-channel communication systems so that enough redundancy is available. The communication network between the national and the State EOCs and the site of the emergency/crises has also been worked out .
It has been observed that at the time of a calamity/disaster, communication services are the first to go out of order. It has therefore been decided to put in place multi-mode and multi-channel communication systems so that enough redundancy is available. The communication network between the national and the State EOCs and the site of the emergency/crises has also been worked out .- Emergency Operation Center plays a vital role in the
Emergency Operation activation.
- It coordinates the flow of information with respect to
activities associated with relief operations.
- During the normal times it maintains a systematic database
of the resources available, important phone numbers, names and addresses
of important government and non-government officials, international
bodies, NGOs.
- During crisis it is expected to function as a center for
decision-making and help flow of information horizontally and vertically
to the respected departments for smoother relief operations.
National Emergency Operations center (NEOC)- To
coordinate the entire disaster/emergency operations effectively, the
existing Control Room at the national level has been being upgraded as
National Emergency Operations center (NEOC).
- The
NEOC is equipped with satellite phones, GPS, computers, emergency lights,
GIS information system etc. in five on-site emergency coordination kits in
ready-to-use mode.
- Staffs
in the NEOC have been trained.
- A
state of the art underground an all-hazard resistant NEOC with superior
structural features and communication facilities has been set up.
The function of control room is not only to control disaster but also to look after rehabilitation and mitigation. No one knows when disaster will strike, so it's better to be prepared from beforehand to reduce loss of life. We can summarize the function of control room in three simple phases:1. Preparation2. Prevention3. MitigationEmergency Operation Center monitors different disaster mitigation programme and co-ordinates with different organization. It also conducts evaluation of the programmes, and immediately takes up necessary measures. Besides, the EOCs may act as control rooms for various other purposes such as law and order problem, elections, VIP movements and other activities requiring coordination.Incident Command System in India.- ICS
was introduced in India during 2003 in order to professionalize
the emergency/disaster response management system in the country by
the adoption of the System as practiced by the USFS. It seeks to
strengthen the existing disaster response management system by
ensuring that the designated controlling/responsible authorities at
different levels are backed by trained Incident Command Teams (ICTs),
whose members have been trained in the different facets of emergency/disaster
response management.
- Given the
territorial jurisdiction in the country, Incident Commanders are in effect
designated for different territorial jurisdictions in advance. In a
Block/Circle, the Block Development Officer/Circle Officer functions as
the Incident Commander. When a incident is of a serious nature or
transcends the boundary of a block, the Sub-Divisional
Officer/Sub-Collector acts as the Incident Commander. In case of a
more complex disaster, the Collector/District Magistrate functions as
Incident Commander. In a widespread calamity where a number of
districts are involved, the State Administration led by the Chief
Secretary and the State Relief Commissioner is involved in mobilizing
resources or deciding priorities.
Describe structural and non-structural mitigation measures in disaster management.Structural Measures to Reduce Disaster RiskNonstructural Measures to Reduce Disaster Risk- Disaster prevention and mitigation
techniques can reduce the economic and social impacts of natural
disasters.
- Structural measures are the most traditional
approach used to reduce disaster risk through proper engineering
practices.
- Examples include designing electrical power
systems and transportation infrastructure to withstand weather and
earthquakes; sinking transmission lines for protection from hurricanes;
and, building levees and dams to minimize floods.
- Other flood mitigation measures include:
construction of floodways, spillways, hydraulic control structures,
dykes, dams, control gates, drainage system improvements (including
river-dredging) and flood detention basins.
- Nonstructural mitigation measures are
non-engineered activities that reduce the intensity of and vulnerability
to hazards.
- Nonstructural mitigation measures include
such activities as land use planning and management; zoning ordinances
and building codes; public education and training; and coastal, upstream
and mountain reforestation.
- Nonstructural measures can be encouraged by
governmental and private-industry incentives, such as preferential tax
codes and deductibles, or by adjusted insurance premiums that reward
private loss-reducing measures.
- Numerous parties can implement nonstructural
mitigation measures: governmental authorities with the power to
legislate and enforce building codes and zoning requirements;
- NGO’s that initiate neighborhood
loss-prevention programs; and private sector enterprises that provide
incentives for loss-reducing measures.
- Nonstructural mitigation measures are
particularly appropriate for developing countries because these remedies
usually require fewer financial resources.
 -------------------------------------------------------------------------Tit - Bits
-------------------------------------------------------------------------Tit - Bits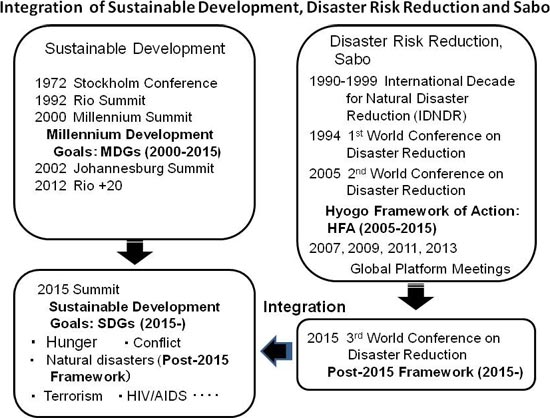
- UN’s World Conference
on Disaster Reduction (WCDR) in Kobe, Japan,
in 2005, only days after the 2004 Indian
Ocean earthquake.
- Hyogo framework for
action (2005-2015)
1. It was adopted by 168 member states of UN at world disaster reduction conference held in Hyogo,Japan in 2005
2.It was first plan to layout road map for governments and different sectors to bolster resilience of nations and communities against disaster and reduce losses.
3.Expected outcome:The substantial reduction of disaster losses, in lives and in the social,economic and environmental assets of communities and countries.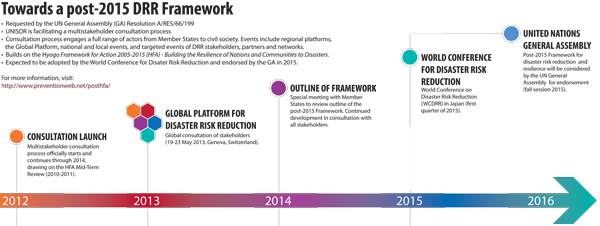

- Vulnerability
is the characteristics and circumstances of a community, system or asset
that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard.

