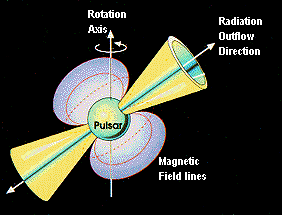
What are PULSARS?
- Pulsars are highly magnetized rotating neutron stars that emit a
beam of electromagnetic radiation in the form of radio waves. Their
observed periods range from 1.4 ms to 8.5 s.
- The radiation can only be observed when the beam of emission is
pointing towards the Earth. This is called the lighthouse effect and gives
rise to the pulsed nature that gives pulsars their name.
- Because neutron stars are very dense objects, the rotation period
and thus the interval between observed pulses are very regular. For some
pulsars, the regularity of pulsation is as precise as an atomic clock.
- Pulsars are known to have planets orbiting them, as in the case of
PSR B1257+12.
- The first pulsar was observed in July 1967 by Jocelyn Bell Burnell
and Antony Hewish.
The Vela Pulsar and its surrounding pulsar wind
nebula.
- In 1974, Joseph Hooton Taylor, Jr. and Russell Hulse discovered,
for the first time, a pulsar in a binary system, PSR B1913+16.
- This pulsar orbits another neutron star with an orbital period of
just eight hours.
- Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that this system
should emit strong gravitational radiation, causing the orbit to
continually contract as it loses orbital energy.
- Observations of the pulsar soon confirmed this prediction,
providing the first ever evidence of the existence of gravitational waves.
As of 2004, observations of this pulsar continue to agree with general
relativity.
- In 1993, the Nobel prize in physics was awarded to Taylor and Hulse
for the discovery of this pulsar.
- In 1982, a pulsar with a rotation period of just 1.6 milliseconds
was discovered, by Shri Kulkarni and Don Backer.
- Observations soon revealed that its magnetic field was much weaker
than ordinary pulsars, while further discoveries cemented the idea that a
new class of object, the "millisecond pulsars" (MSPs) had been
found.
- MSPs are believed to be the end product of X-ray binaries. Owing to
their extraordinarily rapid and stable rotation,
=================================================================================
What are QUASARS ?

- Quasars are compact, quasi-stellar objects. They are very bright
and luminous, trillion of times brighter than the sun.
- A quasar is a whole galaxy that shoots out a beam of energy from
its north and south poles.
- A quasar is powered by a supermassive black hole.
- When matter falls into the black hole, the high speed spinning
causes some of that matter to be ejected as beams of energy.
=================================================================================
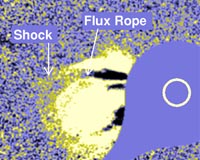
What are FLUX ROPES ?
- Astronomers
have spotted enormous magnetic entities - called flux ropes - stretching
for hundreds of kilometres in Venus's upper atmosphere, above the poles.
- The
European Space Agency's Venus Express spacecraft observed the strange
structures in Venus' atmosphere which has redrawn scientists' perceptions
of the planet's magnetic environment.
- Flux ropes
have been seen before around other planets, including Earth. They
transport superheated plasma gas from one side of the "rope" to
the other.
- On
Earth, flux ropes form near the face of the planet opposite the Sun. The stream of charged particles known as the solar wind flows
around the planet and creates a "magnetotail" of charged
particles on the other side.
- Periodic solar outbursts known as coronal mass ejections arise from
a type of flux rope. The delicate structures sit on top of the Sun and
transport matter and superheated gas from one part of the Sun to
another.
- Venus
stands apart from most other planets in the solar system, however, because
it has no magnetic field. When Venus' atmosphere has a higher
pressure than the incoming solar wind field, the ionosphere is considered
"unmagnetised," meaning that it's free of all but the smallest
magnetic field structures.
- The
ionosphere of Venus stays unmagnetised most of the time, until the solar
wind reaches a higher pressure than the surrounding atmosphere and
magnetises it.
- In these
conditions, relatively small flux ropes can form due to the higher speed
of the solar wind rolling over the slower ionosphere, researchers
said.
- The
ionosphere is filled with these very small kilometres across - flux ropes,
- Scientists
determined that the flux ropes on Venus form from solar particles on the
side of the planet facing away from the Sun, in the magnetotail.
- It seems to
be associated with a process known as reconnection, which is magnetic
field lines joining up together and forming a new magnetic
configuration,giant flux ropes were previously found in the atmosphere of
Mars ? but only in the southern hemisphere. Mars, like Venus, does not
have a planet-wide magnetic field.
- The
observation and formation of the large flux rope at Mars might raise
speculative questions related to the giant flux ropes at Venus.
=================================================================================
What
is a spiral galaxy?

|
========================================================================
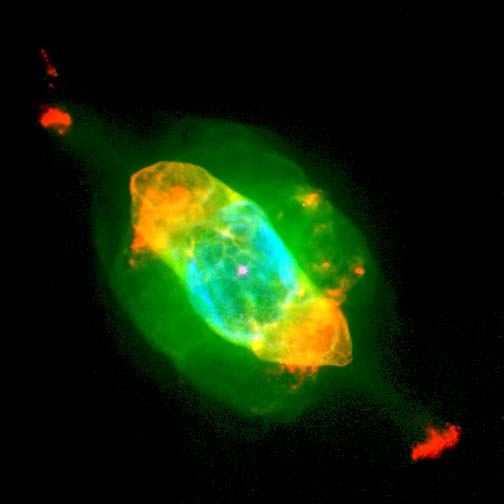
What is a nebula?
- A nebula is a cloud of gas
and dust in space.
- Some nebulas are regions
where new stars are being formed, while others are the remains of dead or
dying stars.
- Nebulas come in many
different shapes and sizes.
- There are four main types of
nebulas: Planetary nebulas, Reflection nebulas, Emission
nebulas, and Absorption nebulas.
- The word nebula comes from
the Latin word for cloud.
========================================================================
What is a comet?
- Comets are basically dusty
snowballs which orbit the sun.
- They are made of ices, such
as water, carbon dioxide, ammonia and methane, mixed with dust.
- These materials came from
the time when the solar system was formed.
- Comets have an icy center
(nucleus) surrounded by a large cloud of gas and dust (called the
coma).
- The coma is created as the
ice in the nucleus is warmed by the sun and vaporizes.
- Comets can develop 2 tails
as they travel closer to the sun, a straight gas tail and a curved dust
tail.
- The gas tail is created by
the solar wind, whose magnetic fields pull the gas away from the comet's
coma.
- The dust in the coma is not
affected by magnetic fields but is vaporized by the sun's heat, and forms
a curved tail which follows the comet's orbit.
=================================================================
What are asteroids?
- Asteroids are rocky-metallic
objects which range in size from about the size of pebbles to around 600
miles (~1,000 km) across.
- Although they orbit the sun,
they are too small to be considered planets. Asteroids are thought to be
leftover material from the formation of our solar system.
- Most are found in the
Asteroid Belt, a doughnut-shaped ring which lies between the orbits of
Mars and Jupiter.
- Astronomers have also
identified a group of asteroids whose orbits cross Earth's orbit.
- Several hundred thousand
asteroids are known to exist in our solar system, and many are yet to be
discovered.
- Most of the undiscovered
asteroids are the smaller ones (less than 100 km across) which are more
difficult to detect.
- It is estimated that there
are over a million of these smaller asteroids.
The largest asteroid is called Ceres. It is about one-quarter the
size of our moon.
=================================================================================

What
is the difference between an asteroid and a comet?
=================================================================================
Can
asteroids have moons?
=================================================================================
|

- NASA
scientists are planning to capture a 5,00,000 kg asteroid, relocate it and
transform it into a space station for astronauts to refuel at on their way
to Mars.
- It would be
the first time a celestial object has ever been moved by humans, a media
report said.
- The White
House's Office of Science and technology will consider the $2.6 billion
plan in the coming weeks as it prepares to set its space exploration
agenda for the next decade.
- The
technology would also open up the possibility of mining other asteroids
for their metals and minerals.
- An
'asteroid capture capsule' would be attached to an old Atlas V rocket and
directed the asteroid between the Earth and the Moon.
- Once close,
the asteroid capsule would release a 50 ft diameter bag that wrap around
the spinning rock using drawstrings, the paper said.
- The craft
would then turn on its thrusters, using an estimated 300 kg of propellant,
to stop the asteroid in its tracks and tow it into a gravitationally
neutral spot.
- Some
asteroids are full of iron which could be used for in the making of new
space stations, others are made up of water which could be broken down
into hydrogen and oxygen to make fuel.