Volcanic eruptions can be violent, passive, or anywhere in between. When a people are told that a volcano is going to erupt, many imagine an explosive eruption with a giant ominous cloud of ash and red hot lava flowing down a mountain. However, since volcanic eruptions can vary greatly in size and intensity, volcanologists use the Volcano Explosivity Index, or VEI, to classify the size of an eruption.
The Volcano Explosivity Index
The VEI scale has been used in modern volcanology as a way to forecast the possible size of a volcanic eruption based on that volcano's historical eruptions.
It first debuted in 1982 as a paper titled "The Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI): An Estimate of Explosive Magnitude for Historical Volcanism," written by Christopher Newhall and Steve Self and published in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
The VEI of a volcano depends mostly on the volume of material ejected during the eruption and the height of the ash column or plume. The VEI scale breaks down volcanic eruptions into nine classifications ranging from a VEI of zero to eight - zero being a non-explosive eruption and eight being a mega-colossal eruption. There are no known explosive events with a VEI greater than eight.
Read more at Suite101: The Volcano Explosivity Index: Scientists Use the VEI Scale to Measure the Impact of an Eruption http://volcanoes.suite101.com/article.cfm/the_volcano_explosivity_index#ixzz0aooybuVZ
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What Is the Rift Valley?
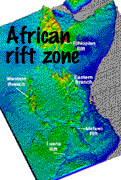 Africa's Great Rift Valley is a 6,000-mile crack (fissure) in the earth's crust, stretching from Lebanon to Mozambique. One of its most dramatic sections slices through East Africa, dividing Kenya into two segments. Geologists know that the Rift Valley was formed by violent subterranean forces that tore apart the earth's crust. These forces caused huge chunks of the crust to sink between parallel fault lines and force up molten rock in volcanic eruptions. Evidence that this process, called rifting, is still in progress comes from the many active and semi-active volcanoes, located along the Rift. Evidence of volcanic activity along the rift is provided by the presence of numerous boiling hot springs.
Africa's Great Rift Valley is a 6,000-mile crack (fissure) in the earth's crust, stretching from Lebanon to Mozambique. One of its most dramatic sections slices through East Africa, dividing Kenya into two segments. Geologists know that the Rift Valley was formed by violent subterranean forces that tore apart the earth's crust. These forces caused huge chunks of the crust to sink between parallel fault lines and force up molten rock in volcanic eruptions. Evidence that this process, called rifting, is still in progress comes from the many active and semi-active volcanoes, located along the Rift. Evidence of volcanic activity along the rift is provided by the presence of numerous boiling hot springs.----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What is Orogenesis?
In its original, literal sense, orogenesis means ‘mountain building’, but today it more specifically refers to the tectonics of mountain building (as opposed to mountain building by erosion).Orogenesis is brought about by the movements of the rigid plates making up the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle (described by plate tectonics).Where two plates collide at a destructive margin rocks become folded and lifted to form chains of mountains (such as the Himalayas).
Processes associated with orogeny are faulting and thrusting , folding, metamorphism, and plutonism .However, many topographical features of mountains – cirques, U-shaped valleys – are the result of non-orogenic processes, such as weathering, erosion, and glaciation.
Isostasy (uplift due to the buoyancy of the Earth's crust) can also influence mountain physiography.
Source--

